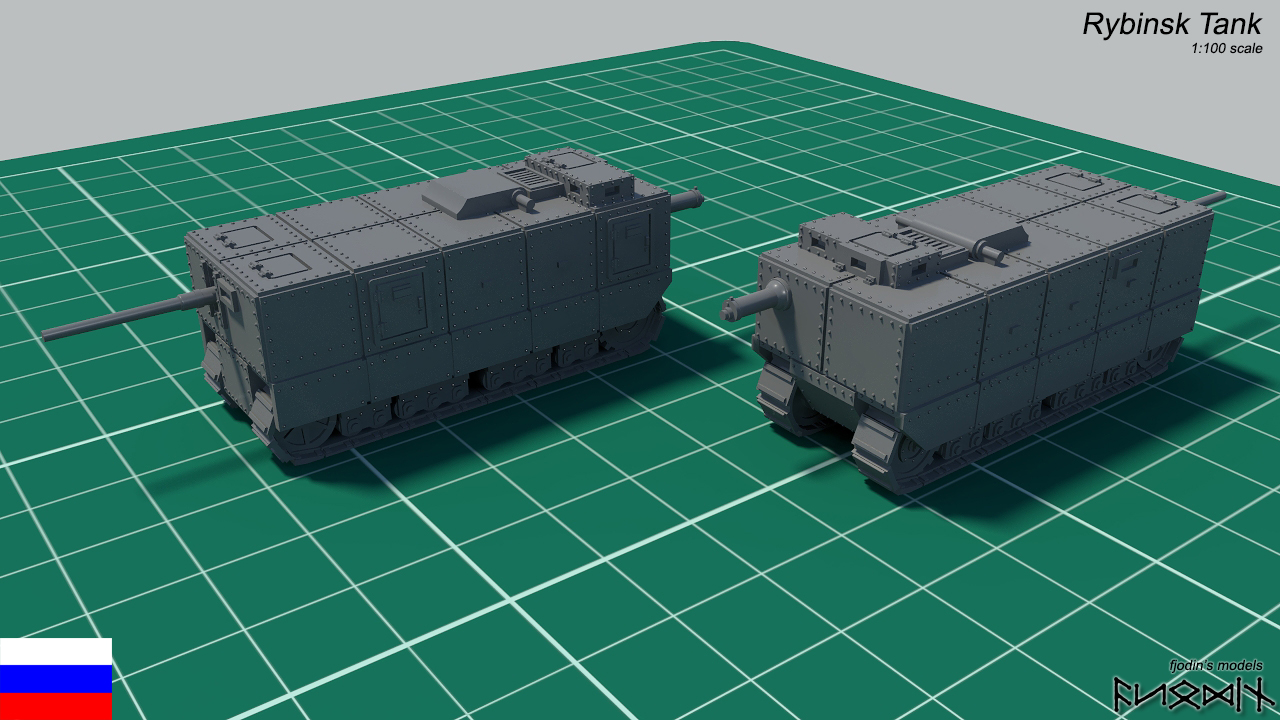
Rybinsk tank It’s the project of a medium tank developed in the Russian Empire in 1915-1917. One of the most mysterious armored projects created in Russia during the First World War – the information about it is very limited and sketchy. According to the most common version, the tank was created using a Holt tractor. There is also reason to believe that the the basis of a Rybinsk tank design was a not adopted project of french Colonel Etienne in 1915.
The initial draft of a tank was proposed to the military department at the end of 1916, but the events of 1917 put an end to further work in this direction.
The tank have unusual layout. It have driver and machine gunner at front of a vehicle but 75mm naval gun at REAR of a vehicle. Tank was intended to be used as infantry support vehicle. Tanks should move at front of advancing infantry lines and use their machine guns to fight the enemy infantry. If they encounter enemy fortifications, tanks should steer and use their rear guns.
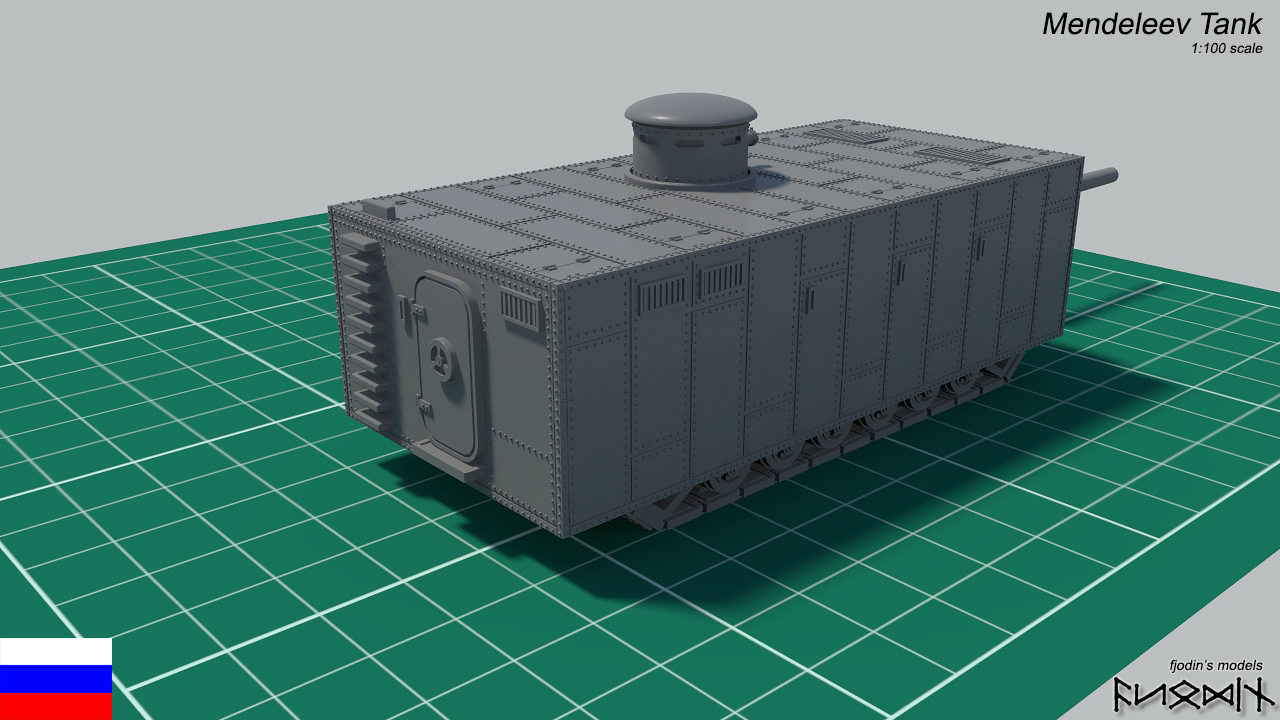
Rybinsk Tank specifications:
Size: 5 meters long, 2 meter tall and wide
Crew: 4
Armor: 12mm front, 10mm rest
Maximum speed: 10-15 km/h on plans but 8 km/h are more realistic because tank have Holt tracks and same weight like French Schneider CA1 tank
Armament: 75mm 1892 canet naval gun
Maxim Machine Gun
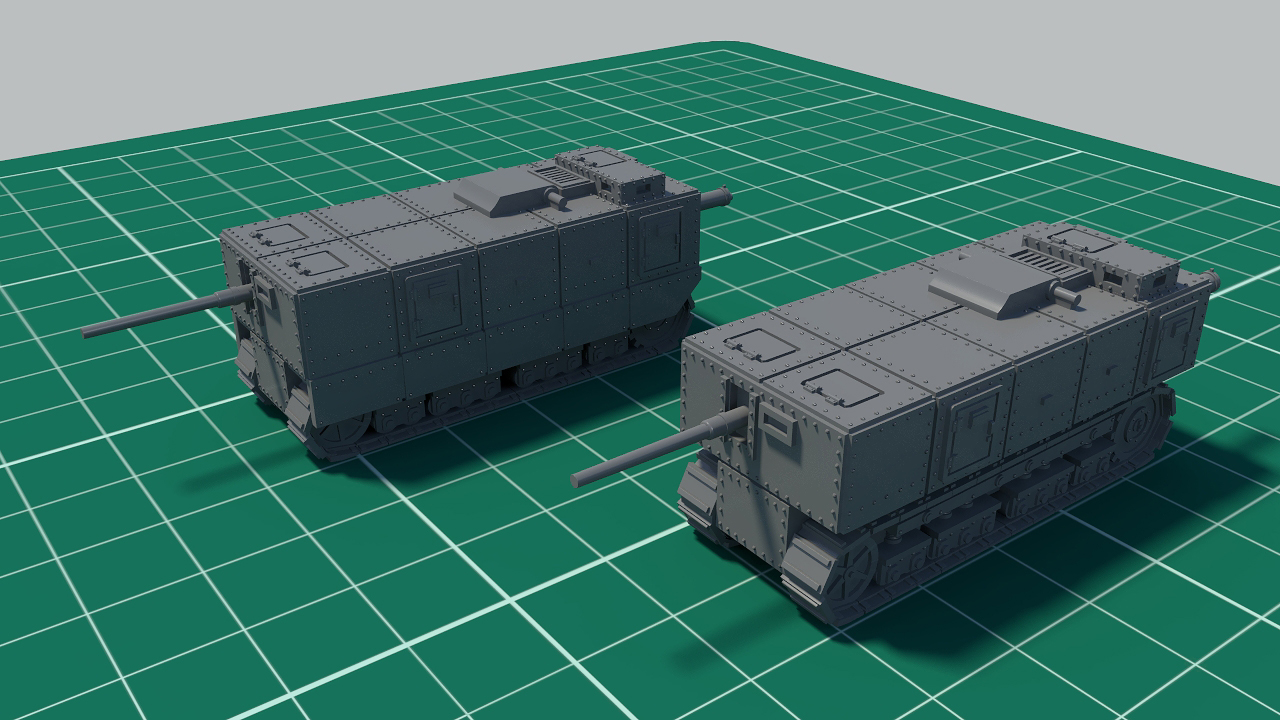
Rybinsk tank with and without skirt.
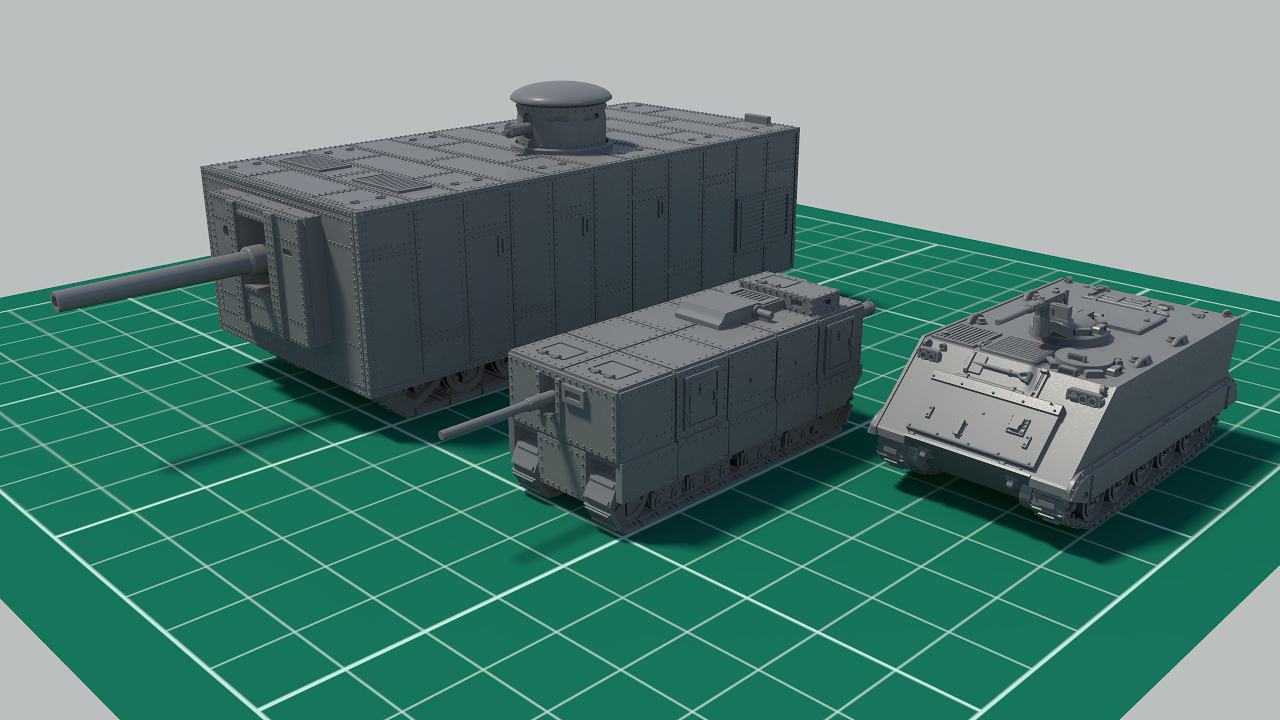
Size comparison between Mendeleev tank, Rybinsk tank and M113.